CONSERVATISM AND COGNITIVE ABILITY
by Lazar Stankov National Institute of Education (NIE, 1 Nanyang Walk, Singapore © 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
NOTICE: THIS WORK MAY BE PROTECTED BY COPYRIGHT
YOU ARE REQUIRED TO READ THE COPYRIGHT NOTICE AT THIS LINK BEFORE YOU READ THE FOLLOWING WORK, THAT IS AVAILABLE SOLELY FOR PRIVATE STUDY, SCHOLARSHIP OR RESEARCH PURSUANT TO 17 U.S.C. SECTION 107 AND 108. IN THE EVENT THAT THE LIBRARY DETERMINES THAT UNLAWFUL COPYING OF THIS WORK HAS OCCURRED, THE LIBRARY HAS THE RIGHT TO BLOCK THE I.P. ADDRESS AT WHICH THE UNLAWFUL COPYING APPEARED TO HAVE OCCURRED. THANK YOU FOR RESPECTING THE RIGHTS OF COPYRIGHT OWNERS.
-- Fox News Worried That Anti-Bullying Measures Are Anti-Conservative, by Amanda Marcotte
-- How to Become a Conservative in Four Embarrassing Steps, by Paul Buchheit
-- Low-Effort Thought Promotes Political Conservatism, by Scott Eidelman, Christian S. Crandall, Jeffrey A. Goodman and John C. Blanchar
-- Why is the Conservative Brain More Fearful? The Alternate Reality Right-Wingers Inhabit is Terrifying, by Joshua Holland
Article history: Received 17 July 2008 Received in revised form 7 December 2008 Accepted 8 December 2008 Available online 3 February 2009
ABSTRACT
Conservatism and cognitive ability are negatively correlated. The evidence is based on 1254 community college students and 1600 foreign students seeking entry to United States' universities. At the individual level of analysis, conservatism scores correlate negatively with SAT, Vocabulary, and Analogy test scores. At the national level of analysis, conservatism scores correlate negatively with measures of education (e.g., gross enrollment at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels) and performance on mathematics and reading assessments from the PISA (Programme for International Student Assessment) project. They also correlate with components of the Failed States Index and several other measures of economic and political development of nations. Conservatism scores have higher correlations with economic and political measures than estimated IQ scores.
Keywords: Conservatism Intelligence Multi-level
1. Introduction
There has been an increased interest in the construct of conservatism. Recent evidence indicates that some existing stereotypes are not supported by the available data. For example, Brooks (2006, 2008) reports that conservatives engage more than liberals in charitable activities and people on the political right are nearly twice as happy as those on the left. The work of Napier and Jost (2008) shows that conservatives tend to be happier than liberals because of their tendency to justify the current state of affairs and because they are less bothered by inequalities in the society. The focus of these investigators is on political conservatism — tendency to attach high importance to topics that are high on the agendas of right-wing political parties within a given society and, consequently, endorse these parties' candidates in elections. For example, a version of the USA Wilson–Patterson Conservatism Scale (WPC; see Wilson, 1973) used in a study reported by Bouchard et al. (2003) contained 28 items that asked participants to state how important topics such as abortion, property tax, gay rights, liberals and immigration are. [1] In the studies reported in the main body of this paper, political conservatism was not examined directly. However, Jost, Glaser, Kruglanski, and Sulloway (2003) suggest that it is time to re-examine the links between political conservatism and a host of individual difference variables. A constellation of these individual difference variables may be called Conservative syndrome. Although an alternative label, psychological conservatism, may be more appropriate if one's aim is to contrast politics and psychology, the term syndrome appears to be adequate for a discourse within the field of psychology itself.
Jost et al.'s (2003) meta-analysis confirms that several psychological variables predict political conservatism. The list includes death anxiety; system instability; dogmatism; intolerance of ambiguity, low openness to experience, and uncertainty; need for order, closure, and negative integrative complexity; and fear of threat and loss of self-esteem. The theory of Jost et al. (2003) treats political conservatism as motivated cognition and builds on a large body of research accumulated since the end of World War II. One antecedent is the approach advocated by Wilson's (1973) dynamic theory that also saw conservatism as a motivated response to uncertainty. The threat or uncertainty may derive from fear of death, anarchy, foreigners, dissent, complexity, novelty, ambiguity, and social change. Responses to these sources of uncertainty include superstition, religious dogmatism, ethnocentrism, militarism, authoritarianism, punitiveness, conventionality, and rigid morality. Wilson postulated that political conservatism derives from genetic sources (anxiety proneness, stimulus aversion, low intelligence, and physical unattractiveness) as well as environmental influences (parental coldness, punitiveness, rigidity, inconsistency, and low social class). Jost et al. (2003) summarize their own position in the following way: “The core ideology of conservatism stresses resistance to change and justification of inequality and is motivated by needs that vary situationally and dispositionally to manage uncertainty and threat.” (p. 339).
In this paper, I examine the hypothesis that low cognitive ability may be related to conservative syndrome (or conservatism, for short) which, in turn, is defined in terms of measures of personality, social attitudes, values, and social norms. There are two ways to arrive at this assumption. First, we can assume that cognitive ability affects conservatism directly. Thus, the perceived threat may vary depending on cognitive level—sources of threat such as complexity, novelty, and ambiguity may be more threatening to those who score low as opposed to those who score high on cognitive tests. Second, we can postulate that there exists an independent process that influences both conservatism and cognitive functioning. A candidate for this role may be mental rigidity. My primary aim in this paper is to present evidence of correlation, not to test these two causal models.
A recent paper by Deary, Batty, and Gale (2008) provides developmental evidence for a link between intelligence assessed at the age of 10 and anti-traditional and liberal social attitudes (i.e., the opposite of conservatism) at age 30. They report the results of a structural equation modelling analysis that shows a significant direct path coefficient of .46 between a general cognitive factor g and a latent attitude trait they label as Liberal Non-traditional Social Attitudes.
1.1. Conservatism across the domains of Personality, Social Attitudes, Values and Social Norms
Our approach differs from previous work in the way we define and measure the construct of conservatism. This construct emerged, somewhat unexpectedly, in three studies (see Method section for further detail). The first study was designed to assess cross-cultural differences on a set of measures from the domains of Personality, Social Attitudes, Values and Social Norms. Measures from these domains have been used in previous studies of others and cross-cultural differences have been reported but no single study covered all four domains. Most of the information to be reported here derives from this first study (see Stankov & Lee, 2008). The second and the third study (see Stankov, 2007) were based on the US samples only. Structural (i.e., factor-analytic) results of these latter studies proved to be in agreement with the results of the first study.
In our work, conservatism is captured by a score — usually a factor score — obtained from several scales that were not developed specifically for the measurement of conservatism. Thus, it incorporates measures of Personality (Big Five from IPIP), Social Attitudes (Saucier, 2000; Stankov & Knežević, 2005), Values (Schwartz & Bardi, 2001), and Social Norms (GLOBE; House, Hanges, Javidan, Dorfman, & Gupta, 2004) — a total of 43 different subscale scores. Nevertheless, our analyses show the presence of a factor of Conservatism that has loadings from subscales from all these domains and captures many constructs that are included in the nomological net of Jost et al. (2003) and Wilson (1973). This factor is expected to correlate with cognitive ability for reasons outlined above.
What are the other factors that emerge from the analysis of 43 subscales? Are they also expected to correlate with cognitive ability? Stankov (2007) found three domain-related factors. They are quite different from the Conservatism factor in that they show very little overlap between the domains. These are:
• Personality/Social Attitudes. This is usually a bipolar factor contrasting Personality traits on the negative side and Social Attitudes on the positive side. Loadings of Personality traits on this factor are typically lower than loadings from the Social Attitudes measures. In some of our analyses, this factor splits into a separate Personality factor representing “good” evaluative processes (or perhaps social desirability) and a Social Attitudes factor representing anti- or amoral attitudes towards social objects (Stankov & Knežević, 2005).
• Values. See Method section for the interpretation of this factor.
• Social Norms. Several Social Norms scales from GLOBE study (House et al., 2004) load on this factor.
In this paper I report the analyses based on a smaller (22) number of variables that correspond quite closely to the solution obtained with the full set of 43 measures. Smaller number of variables is employed in order to carry out simultaneous (i.e., multilevel) structural equation modelling of individual- and country-level data that has not been reported in the past.
There is no empirical evidence or theoretical arguments in the literature that suggest a relationship between cognitive ability and Values or Social Norms. [2] Thus, it is reasonable to assume that these two constructs do not correlate with cognitive measures. The situation is different with the Personality/ Social Attitudes dimension. Jost (2006) reports that Conscientiousness (positively) and Openness to Experience (negatively) correlate with Democrat/Republican voting preferences of the states within the U.S., interpreted as reflections of liberal/conservative tendencies. Openness to Experience is also known to correlate about .30 with measures of intelligence (Stankov, 2005; Stankov and Lee, 2008). The other side of this bipolar factor, Social Attitudes, captured by Toughness, Maliciousness, and Betaism (i.e., non-PC motives for behavior), have qualities reminiscent of Dogmatism and Authoritarian personalities that are often seen as components of conservatism (see Jost et al., 2003). Since in our work they define a factor that is separate from conservatism, it is reasonable to assume that there is a separation between thuggish and rough Social Attitudes trait and Conservative syndrome that captures not only social attitudes but also Values, Social Norms, and Personality traits. These rough social attitudes are also likely to be related to cognitive ability—they often reflect difficulties or disinclination to make fine-grained analysis of a problematic situation (see Wilson, 1973).
1.1.1. Individual-level and country-level conservatism
Our work that led to the finding of the above four factors was motivated in part by interest in cross-cultural comparisons. In one of our studies, the participants came from both the U.S. and foreign countries. Within the tradition of cross-cultural psychology, total variances on measures of interest are split into two components — within level (or individual level) and between level (or country level). The country level variance–covariance matrix can be arrived at by calculating an aggregate measure such as arithmetic mean for all participants from a given country (see Hofstede, 2001). Thus, each of the 35 countries in our cross-cultural study will have a score on each of the 22 measures employed in this study, and a data reduction procedure like factor analysis can be applied to this 35 by 22 matrix. One issue of interest is whether the structures at individual and country levels are the same or different. If they are the same, it can be concluded that the same influences operate at both levels. If different, the assumption has to be that influences are not the same and the argument may be that the country level, not individual level, structure reflects true cultural differences.
Since our interest is in the relationship between conservatism and cognitive ability, the between-countries scores provide an opportunity to examine the same question from the cross-cultural perspective. Thus, if countries differ in terms of conservatism, how are these differences related to measures of countries' cognitive performance and educational achievements? What may be the cause(s) of country-level differences in conservatism?
While the individual level of analysis focuses on important psychological issues, the country-level analysis brings into focus important social policy issues. Together, they point to a link between psychological and political processes that has been neglected since the 1970s (Jost, 2006). The evidence for the existence of such a link at the country level is important since it may guide decisions related to the deployment of resources.
Apart from showing the link between cognitive performance and conservatism, country-level analyses allow for the examination of broader issues. For example, they provide for an opportunity to examine the relationship of these two constructs with other country-level measures, including various economic and social indicators.
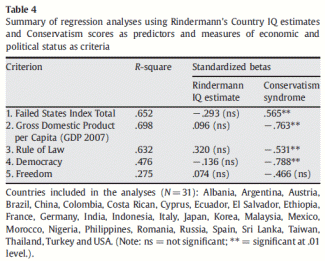
The link between IQ, economic measures of wealth and a host of other variables has been explored extensively. For example, according to Kanazawa (2006; p. 593) the mean Pearson's product-moment correlation between national IQ and various measures of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) across numerous years among the 185 nations that is reported by Lynn and Vanhanen (2002, pp. 110–116) is .577. Lynn and Vanhanen (2006) interpret these correlations as showing that IQ is an important factor contributing to the differences in national wealth and rates of economic growth. Rindermann (2007; Table 4, p. 686) reported correlations between the sum of several cognitive ability measures and GDP in year 1998 to be .63. In his subsequent papers (Rindermann, 2008a,b) he also reports correlations between IQ estimates and country-level measures of education, democracy, the rule of law and many other economic and social indicators.
Similar country-level correlations between Conservatism and economic and social indicators do not exist in the literature. If they turn out to be of the same order of magnitude, shall we assume that Conservatism is another “important determinant” like IQ? Our data will allow us to address this issue.
I employ structural equation modelling and multi-level procedures (Muthén, 1994) and regression analysis to examine the nature of conservatism at both the individual and country levels.
1.1.2. Aims
My aims in this paper are threefold. First, I present structural evidence for the existence of stable factors at both the individual- and country-levels of analysis. Although the overall structure at the individual and country levels may differ, a conservatism factor is expected to emerge at both levels. Second, correlations between factor scores from both levels of analysis with individual- and country-level cognitive measures are presented. Individual cognitive measures are scores on typical aptitude tests. Country-level proxies for cognitive measures are both statistics regarding educational enrolment and scores from the objective achievement tests. My expectation is that the strength of the individual- and country-level conservatism will be negatively correlated with cognitive ability scores. Third, I report on the relationship between Conservatism and a host of country-level economic and sociological variables. The aim is to compare predictive validities of IQ and Conservatism scores.
2. Method
2.1. Participants
The findings to be reported in this paper derive from three studies, all of which employed the same set of measures from the four domains of Personality, Social Attitudes, Values, and Social Norms. The first study (N=1600) was a cross-cultural study with participants from 73 countries. These were the people who took the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL iBT) as a prerequisite for enrolment, mostly in graduate schools, at U.S. universities. The samples of participants from different countries are not representative and may differ from the parent population in many ways. After taking TOEFL, they were asked to participate in a separate survey for a $20 payment. The second (N=430) and third (N=824) studies employed students from 22 community colleges from across the U.S. The data presented in Table 1 are based on the first and second studies. I added the second sample to the first sample (1600+430) and removed from this total sample all those participants who came from the countries that had less than 9 participants. The findings in Table 1 are based on 1895 participants who came from 35 different countries, each having at least 9 participants.
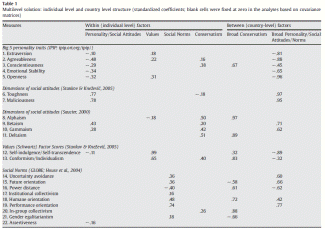
Table 1: Multilevel solution: individual level and country level structure (standardized coefficients; blank cells were fixed at zero in the analyses based on covariance matrices)
The three studies are treated separately because each contained different cognitive measures. A sample of participants in the first study (N=288) also took an Analogies test. All participants in the second study took a Synonyms Vocabulary test, and a sample (N=732) from the third study provided information about their SAT total scores.
2.2. Measures
A total of 316 items that formed 43 scale scores embedded in 6 different instruments was employed. They were all delivered over the Internet in English. To work with a manageable number of variables, the original larger 43- variable data set was reduced to a smaller (22-variable) data set in this paper. The reduction is based on the elimination of 12 variables with missing data and on the replacement of 11 scales of Schwartz's Value Survey (SVS) with 2 factor scores.
2.2.1. Domain: Personality traits
For the measurement of Big Five personality factors (e.g., Saucier & Goldberg, 2002), I used a 50-item scale available from the International Personality Item Pool (IPIP; may be accessed on the Web at ipip.ori.org/ipip/).
1. Extraversion
2. Agreeableness
3. Conscientiousness
4. Emotional Stability (vs. neuroticism).
5. Openness.
2.2.2. Domain: Social Attitudes
Toughness and maliciousness. These two scales are based on work designed to examine demographic and psychological aspects of antisocial and criminal behavior in Serbia during the early 1990s. Stankov and Knežević's (2005) study compared performance of Serb and Australian students on these scales. Measures used in the present study are derived from that earlier work. A 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) was employed.
6. Toughness (machismo, hard realism, street wiseness, Machiavelianism). Example: “I cannot accept any restrictions or rules.”
7. Maliciousness (poor impulse control, sadism, resentment, brutality). Example: “If I had complete power over people, many would regret the day they were born.”
I first met Weev in an online chat room that I visited while staying at Fortuny’s house. “I hack, I ruin, I make piles of money,” he boasted. “I make people afraid for their lives.” On the phone that night, Weev displayed a misanthropy far harsher than Fortuny’s. “Trolling is basically Internet eugenics,” he said, his voice pitching up like a jet engine on the runway. “I want everyone off the Internet. Bloggers are filth. They need to be destroyed. Blogging gives the illusion of participation to a bunch of retards. . . . We need to put these people in the oven!”
I listened for a few more minutes as Weev held forth on the Federal Reserve and about Jews. Unlike Fortuny, he made no attempt to reconcile his trolling with conventional social norms. Two days later, I flew to Los Angeles and met Weev at a train station in Fullerton, a sleepy bungalow town folded into the vast Orange County grid. He is in his early 20s with full lips, darting eyes and a nest of hair falling back from his temples. He has a way of leaning in as he makes a point, inviting you to share what might or might not be a joke.
As we walked through Fullerton’s downtown, Weev told me about his day — he’d lost $10,000 on the commodities market, he claimed — and summarized his philosophy of “global ruin.” “We are headed for a Malthusian crisis,” he said, with professorial confidence. “Plankton levels are dropping. Bees are dying. There are tortilla riots in Mexico, the highest wheat prices in 30-odd years.” He paused. “The question we have to answer is: How do we kill four of the world’s six billion people in the most just way possible?” He seemed excited to have said this aloud.
Ideas like these bring trouble. Almost a year ago, while in the midst of an LSD-and-methamphetamine bender, a longer-haired, wilder-eyed Weev gave a talk called “Internet Crime” at a San Diego hacker convention. He expounded on diverse topics like hacking the Firefox browser, online trade in illegal weaponry and assassination markets — untraceable online betting pools that pay whoever predicts the exact date of a political leader’s demise. The talk led to two uncomfortable interviews with federal agents and the decision to shed his legal identity altogether. Weev now espouses “the ruin lifestyle” — moving from condo to condo, living out of three bags, no name, no possessions, all assets held offshore. As a member of a group of hackers called “the organization,” which, he says, bring in upward of $10 million annually, he says he can wreak ruin from anywhere....
I asked about the status of Weev’s campaign against humanity. Things seemed rather stable, I said, even with all this talk of trolling and hacking.
“We’re waiting,” Weev said. “We need someone to show us the way. The messiah.”
“How do you know it’s not you?” I asked.
“If it were me, I would know,” he said. “I would receive a sign.”
Zeno of Elea, Socrates and Jesus, Weev said, are his all-time favorite trolls. He also identifies with Coyote and Loki, the trickster gods, and especially with Kali, the Hindu goddess of destruction. “Loki was a hacker. The other gods feared him, but they needed his tools.”
--The Trolls Among Us, by Mattathias Schwartz
Saucier's “-isms.” Saucier's (2005) 28-item questionnaire measuring the four dimensions below was employed. The rather uncommon labels for these scales are based on Saucier's writings. The instrument employs a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (strongly and completely disagree) to 5 (strongly and completely agree).
8. Alpha scale reflects the degree to which an individual subscribes to conventional religious beliefs (Legalism, Institutionalism, Secularism, Evolutionism). Example: “Religion should play the most important role in civil affairs.”
9. Beta scale reflects the degree to which an individual subscribes to various justifications of self-interest (non-PC motives for behavior: Materialism, Sensualism, Fascism). Example: “Worldly possessions are the greatest good in life.”
Finally, we occasionally blog about products, such as films, music, books, and food. All products were donated to us by their authors and distributors. They paid us copious sums of money to write favorable reviews, and we complied. As a result, we're rich! Consequences, schmonsequences, as long as we're rich.
-- About Popehat.com, by Ken White
10. Gamma scale reflects the degree to which an individual subscribes to patriotism, constitutionalism, humanism, existentialism, neoliberalism, and functionalism (sometimes referred to as Western democracy beliefs). Example: “I love and am devoted to my country.”
11. Delta scale reflects the degree to which an individual subscribes to subjective experiences, including paranormal experiences (sometimes referred to as personal mysticism: Hinduism, Transcendentalism, Zen Buddhism, Animism). Example: “Some objects have magical powers.”
Social attitudes captured by both Stankov and Knežević's and Saucier's measures are of the antisocial rather than prosocial variety. Stankov and Knežević (2005) refer to these as “Amoral Social Attitudes.”
2.2.3. Domain: Values
Schwartz and Bardi (2001) developed Schwartz's Values Survey (SVS), a theory of human values postulating 11 basic dimensions along which societies may be differentiated. The Value Survey is used to assess how important each value is as a guiding principle in one's own life. A total of 57 items are rated on a 9-point Likert-type scale ranging from −1 (opposed to my values), 0 (not relevant) to 7 (of supreme importance), and those items were classified into 11 scales having three to eight items each. The 11 scales are as follows: Power (assessing the importance of authority, wealth, social power, public image and social recognition); Achievement (assessing the importance of ambition, success, capacity, influence, and intelligence); Hedonism (assessing the importance of pleasure and enjoyment of life); Stimulation (assessing the importance of variety and excitement); Self-direction (assessing the importance of creativity, freedom, independence, and curiosity); Universalism (assessing the importance of broadmindedness, social justice, equality, and the world at peace); Benevolence (assessing the importance of helpfulness, loyalty, forgiveness, honesty, and responsibility); Traditionalism (assessing the importance of respect for tradition, humility, devoutness, and moderation); Conformity (assessing the importance of obedience, self-discipline, and politeness); Security (assessing the importance of social order, family security, national security, and sense of belonging); and Spirituality (assessing the importance of meaning of life, sense of inner harmony, and sense of detachment). The main reason for using factor scores instead of the scales themselves derives from a need to reduce the number of variables in the battery.
Stankov and Knežević (2005, p. 122) and Stankov (under review A) carried out exploratory factor analyses of the SVS and obtained two factors. I employ the factor scores from Stankov (under review A) in the analyses of this paper. The interpretation of the two factors is as follows:
12. Self-indulgence/Self-transcendence. The variables that define this factor include Self-directedness, Stimulation and Hedonism, all of which represent individualistic, self-indulging value orientations. The other three variables — Benevolence, Spirituality, and Universality — are not primarily individualistic. They indicate a focus on social context outcomes, implying a value orientation that is sometimes referred to as Self-transcendence. Thus, the factor indicates value orientations that combine a tendency to enjoy life on one hand and, at the same time, be charitable to others and appreciate the broader social context of life.
13. Conformism/Individualism. The variables that define this factor are Traditionalism, Conformism, and Security, all of which indicate a conservative value orientation. However, this orientation is also characterized by Power (social power, social recognition) and Achievement (ambition, success, influence), both of which are indicative of an individualistic value orientation.
2.2.4. Domain: Social Norms
There are nine main Social Norm dimensions that emerged from the GLOBE research project (e.g., House et al., 2004). All statements were prefaced with “In my society…” and the participant had to answer on a 7-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (strongly agree) to 7 (strongly disagree). A total of 39 statements are used to assess:
14. Uncertainty Avoidance. (The extent to which members of an organization or society strive to avoid uncertainty by relying on established social norms, rituals, and bureaucratic practices). Example: “Most people lead highly structured lives with few unexpected events.”
15. Future Orientation. (The degree to which individuals in organizations or societies engage in future-oriented behaviors such as planning, investing in the future, and delaying individual or collective gratification). Example: “Most people live for the present rather than the future.”
16. Power Distance (The degree to which members of an organization or society expect and agree that power should be stratified and concentrated at higher levels of an organization or government). Example: “Followers are expected to obey their leaders without question.”
17. Institutional Collectivism (The degree to which organizational and societal institutional practices encourage and reward collective distribution of resources and collective action.) Example: “Leaders encourage group loyalty even if individual goals suffer.”
18. Humane Orientation (The degree to which individuals in organizations or societies encourage and reward individuals for being fair, altruistic, friendly, generous, caring, and kind to each other.) Example: “People are generally very tolerant of mistakes.”
19. Performance Orientation (The degree to which an organization or society encourages and rewards group members for performance improvement and excellence.) Example: “Students are encouraged to strive for continuously improved performance.”
20. In-Group Collectivism. (The degree to which individuals express pride, loyalty, and cohesiveness in their organizations or families.) Example: “Employees feel great loyalty toward their organization.”
21. Gender Egalitarianism (The degree to which society minimizes gender role differences while promoting gender equality.) Example: “Boys are encouraged more than girls to attain higher education.”
22. Assertiveness (The degree to which individuals in organizations or societies are assertive, confrontational, and aggressive in social relationships.) Example: “People are generally dominant in their relationships with each other.”
3. Results
3.1. Individual- and country-level structure
Table 1 presents the outcome of the multilevel factor analysis carried out with Mplus (Muthén & Muthén, 2005) software. Multilevel analysis fits simultaneously within-individual and between-countries covariance matrices. The left side in Table 1 shows individual-level factor loadings, and the right side presents between-countries factor loadings. All coefficients in this table are standardized — they correspond to significant coefficients in the fitted covariance matrices solution. The overall goodness-of-fit statistics for this model are acceptable to good, e.g., the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) being equal to .057.
The individual-level structure is in agreement with several other factor analytic results from our laboratory. The factors are:
1. Personality/Social Attitudes. This is a bipolar factor with (Amoral) Social Attitudes (Toughness, Maliciousness, Betaism, and Gammaism) at the positive pole and personality at the negative pole. In this analysis, low negative loadings from Self-Indulgence/Transcendence and Assertiveness are also present on this factor. This, however, is not a common finding in our work. Negative loadings from Personality are lower in size than positive loadings from the other measures. Those having high scores on this factor can be described as psychologically rough people (e.g., agreeing with tough, malicious statements, low on agreeableness and expressing politically noncorrect views).
2. Values. The highest loadings on this factor are from the factor scores representing the two Values dimensions that underlie Schwartz's Values Survey (SVS). If all 11 SVS scales were to be included in the analyses, a single Values factor would appear, and loadings from the personality scales (Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Openness) and Alphaism would be much smaller or nonexistent on this factor (Stankov, under review A).
3. Social Norms. Seven out of nine GLOBE measures define this factor, and there are no other significant loadings.
4. Conservatism. This factor is defined by the four Saucier's measures: Social Attitudes (largely by two: Alphaism and Deltaism), the Conformism/Individualism factor from the domain of Values, the Personality factor of Conscientiousness, and In-Group Collectivism from the domain of Social Norms. The presence of loadings from Agreeableness and (negative) Toughness is not a common finding with this factor. It should be kept in mind that all individual-level analyses for the three studies that provided cognitive measures reported in Table 2 below contained core conservatism scores, but, as expected, the actual loadings varied from study to study (see footnotes in Table 2).
The Between-countries analysis produced two factors:
1. Broad Conservatism factor. As can be seen on the right side of Table 1, the first factor has loadings from Alphaism (religious sources of authority), Deltaism (personal spiritualism), In-Group Collectivism, Conscientiousness, and Conformism/Individualism. All these are the core variables of conservatism at the individual level. In addition, this factor has loadings from four Social Norms measures and Self-Indulgence/Self-Transcendence that were not a part of the Conservatism factor at the individual level. Thus, the between-countries factor of Conservatism is somewhat broader than the corresponding individual-level factor; it captures a bit of variance from Social Norms and Values that is not captured by the individual-level factor.
2. Broad Personality/Social Attitudes/Social Norms factor. This, again, is a bipolar factor, with all Personality measures in addition to Values factors (Self-Indulgence/Self-Transcendence and Conformism/Individualism) and Power Distance having negative loadings. Positive loadings are from Social Attitudes (Toughness, Maliciousness, Betaism, and Gammaism) and from four Social Norms factors. Thus, although the core of this between-countries factor resides in Personality and Social Attitudes, it is again broader than the corresponding within-individual factor because it captures Values and Social Norms.
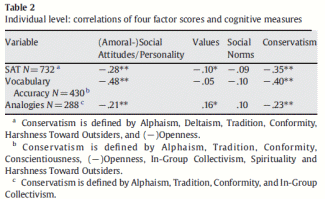
Table 2: Individual level: correlations of four factor scores and cognitive measures
a Conservatism is defined by Alphaism, Deltaism, Tradition, Conformity, Harshness Toward Outsiders, and (−)Openness.
b Conservatism is defined by Alphaism, Tradition, Conformity, Conscientiousness, (−)Openness, In-Group Collectivism, Spirituality and Harshness Toward Outsiders.
c Conservatism is defined by Alphaism, Tradition, Conformity, and In-Group Collectivism.
The two between-countries factors correspond largely to Conservatism and Personality/Social Attitudes individual-level factors, with Values and Social Norms split about equally between them. Factor scores on the two between-countries factors are used in the analyses reported in Table 3.
Factor inter-correlations at the individual level are generally low and different from zero for Conservatism factor only. Thus, Conservatism correlates .39 with the Values factor and .22 with the Social Norms factor. As expected, Conservatism has negative and low correlation (−.211) with the Personality/Social Attitudes factor. At the country-level, correlation between the two broad factors was fixed at zero in the fitted solution.